Portfolio
Selected Projects
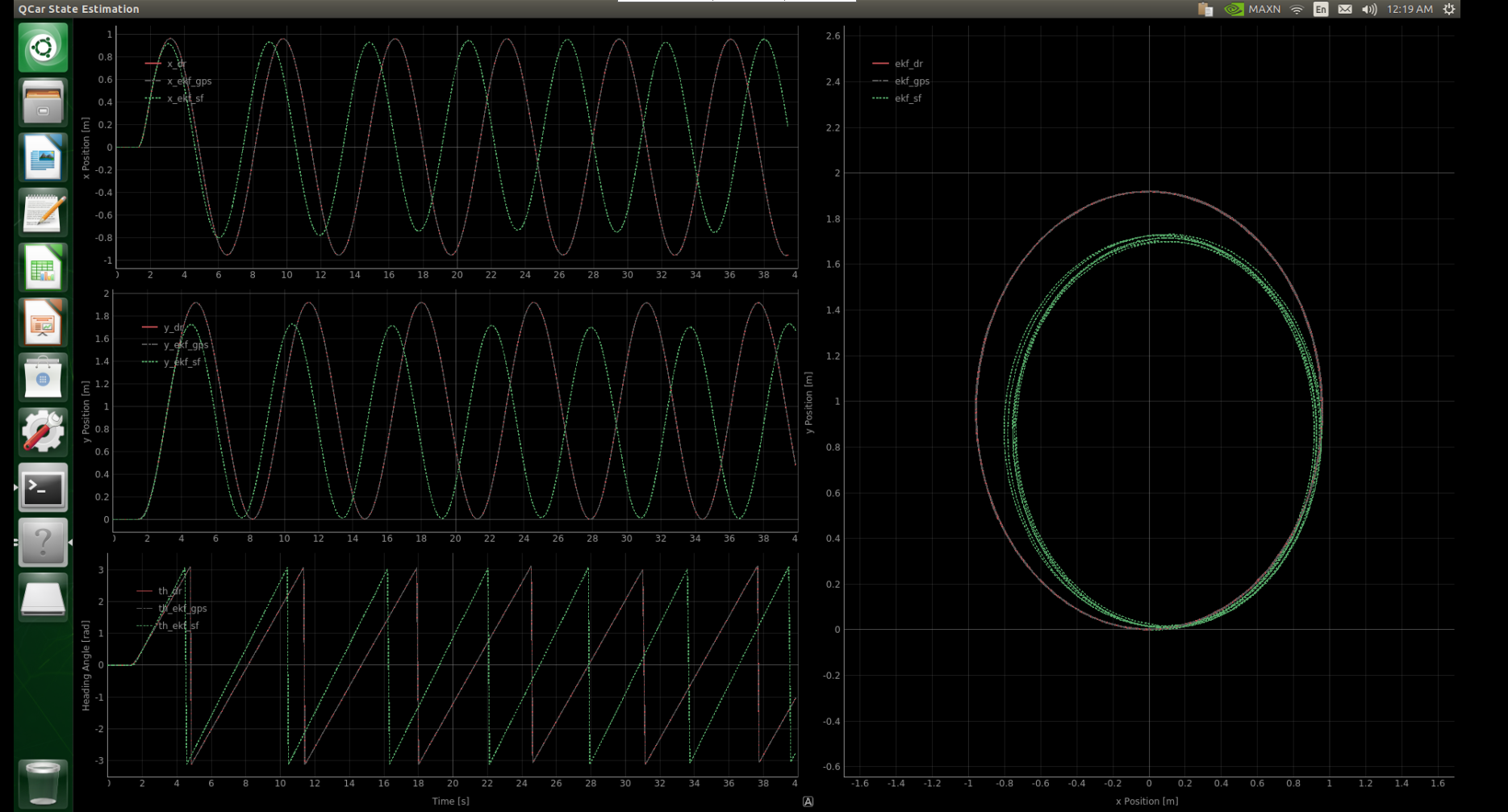
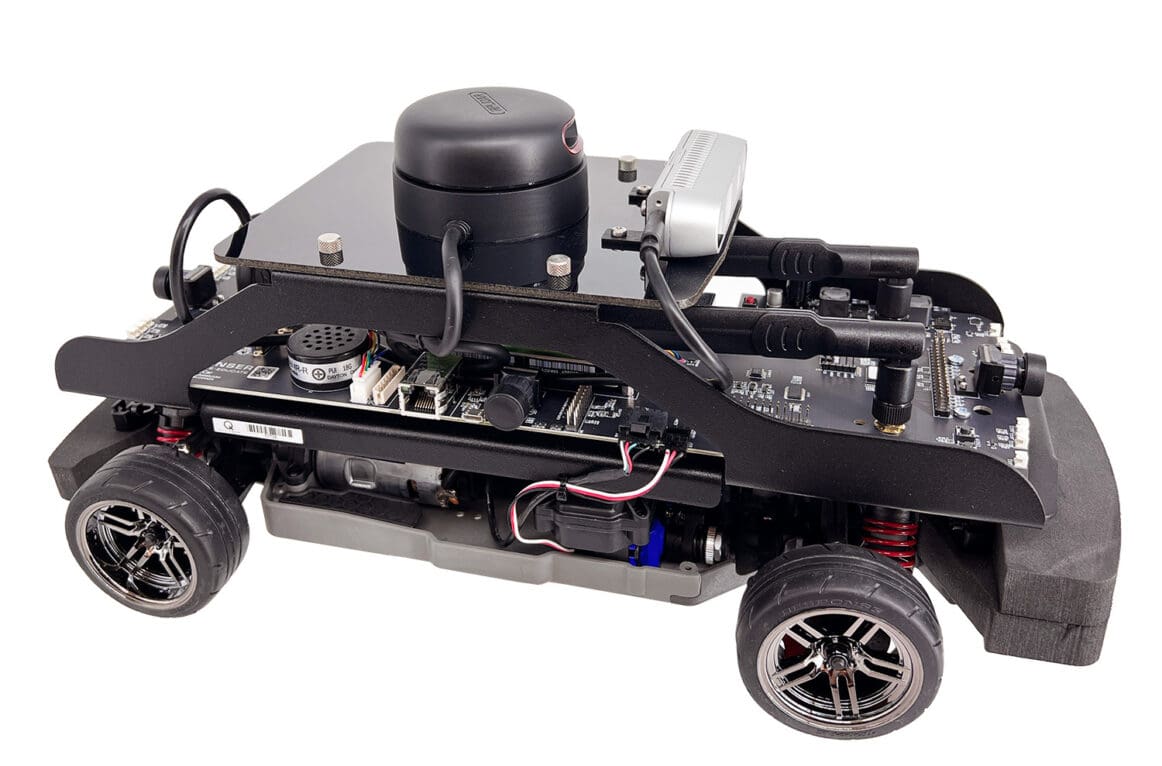 | QCar Control and Estimation Framework This project implements a control and estimation framework for a QCar system, leveraging sensor fusion techniques with Kalman Filters (KF) and Extended Kalman Filters (EKF). The system integrates data from gyroscopes, GPS, and motor tachometers to estimate the state of the vehicle, including position, heading angle, and sensor biases. To ensure precise motion control, the system employs a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. The PID controller regulates vehicle speed and steering angle by dynamically adjusting control inputs based on real-time state estimates. |
 | Multi-Layer Neural Network-Based Optimal Adaptive Tracking Control of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles We propose a novel deep reinforcement learning-based optimal adaptive tracking control framework for nonlinear discrete-time UAV systems with partially uncertain dynamics. The approach employs an actor-critic multilayer neural network (MNN) to approximate the value function and optimize the UAV control policy. A hybrid learning scheme is introduced, where the critic MNN weights are updated in real-time at each sampling instant and refined iteratively between instants to accelerate convergence. To mitigate the persistency of excitation (PE) condition, a replay buffer is incorporated into the critic update law using concurrent learning, improving sample efficiency and control robustness. This approach enhances UAV tracking accuracy while reducing cumulative control cost, ensuring robust performance under uncertainty. |
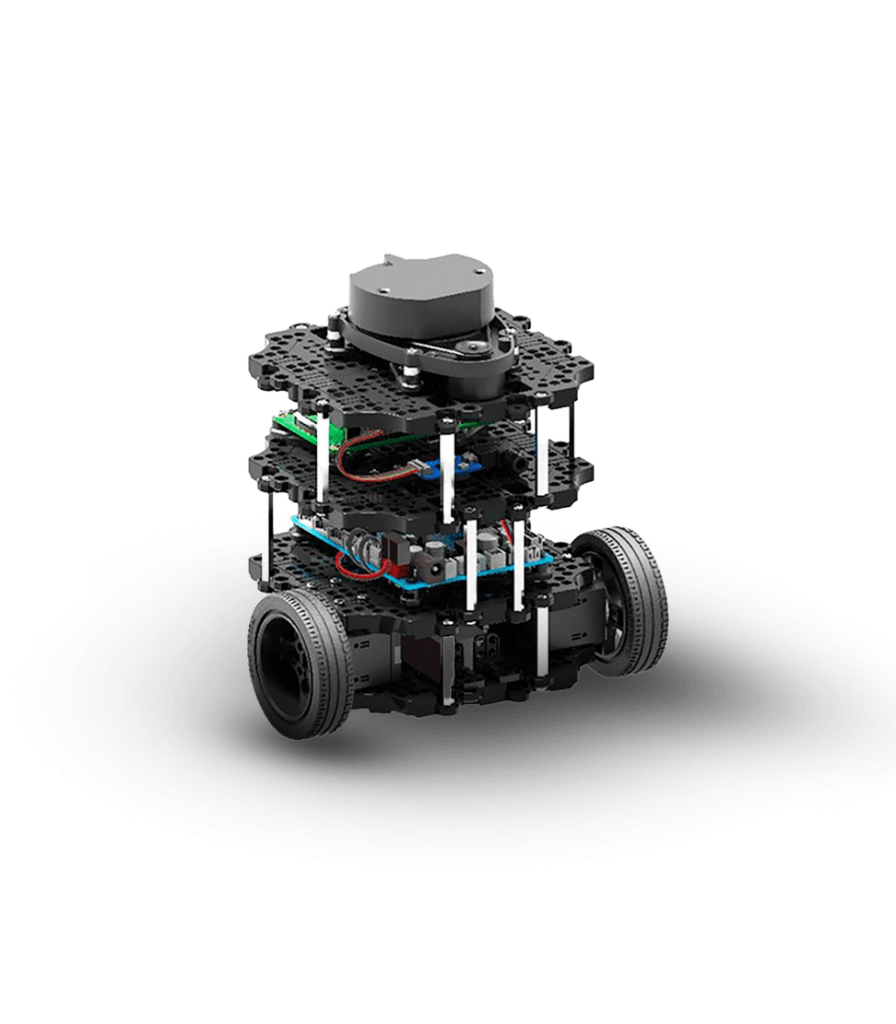 | Bumperbot: ROS2-Based Mobile Robot Control & Estimation This project focuses on the development and simulation of a mobile robot (Bumperbot) using ROS2, integrating motion control, sensor fusion, and state estimation. The robot’s dynamics and hardware configuration were defined using URDF, and the ros2_control plugin was implemented for real-time actuation. Simulation was conducted in Gazebo, providing a realistic environment for testing. The robot is controlled via a joystick, interfaced with ROS2 for seamless manual operation. For autonomous capabilities, an IMU and wheel encoders were utilized, with an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) fusing sensor data for accurate state estimation. This allowed for precise localization and motion control. Key Features:
|
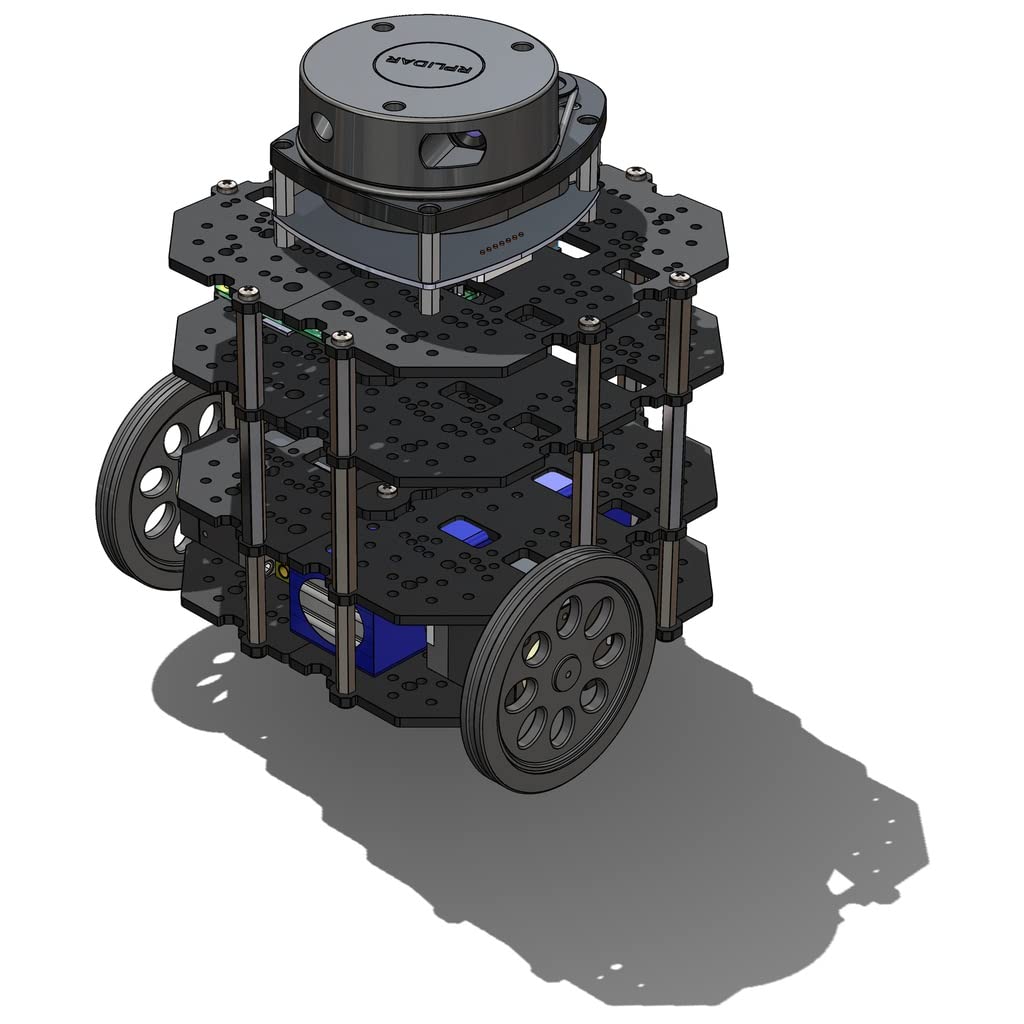 | ROS 2 Global Planners (C++ Implementation) This project focuses on the algorithmic core of autonomous navigation. Rather than relying on pre-built packages, I implemented Dijkstra and A* (A-Star) path planning algorithms from scratch in C++. These planners operate as standalone ROS 2 nodes, subscribing to /map and /goal_pose to calculate optimal trajectories in real-time. The implementation handles raw OccupancyGrid data, transforming world coordinates to grid indices to build a graph representation of the environment. I utilized standard C++ optimization techniques (priority queues, custom comparators) to ensure efficient pathfinding. The nodes also publish visualization data, allowing for real-time debugging of the search frontier (visited nodes) versus the final calculated path in RViz. |
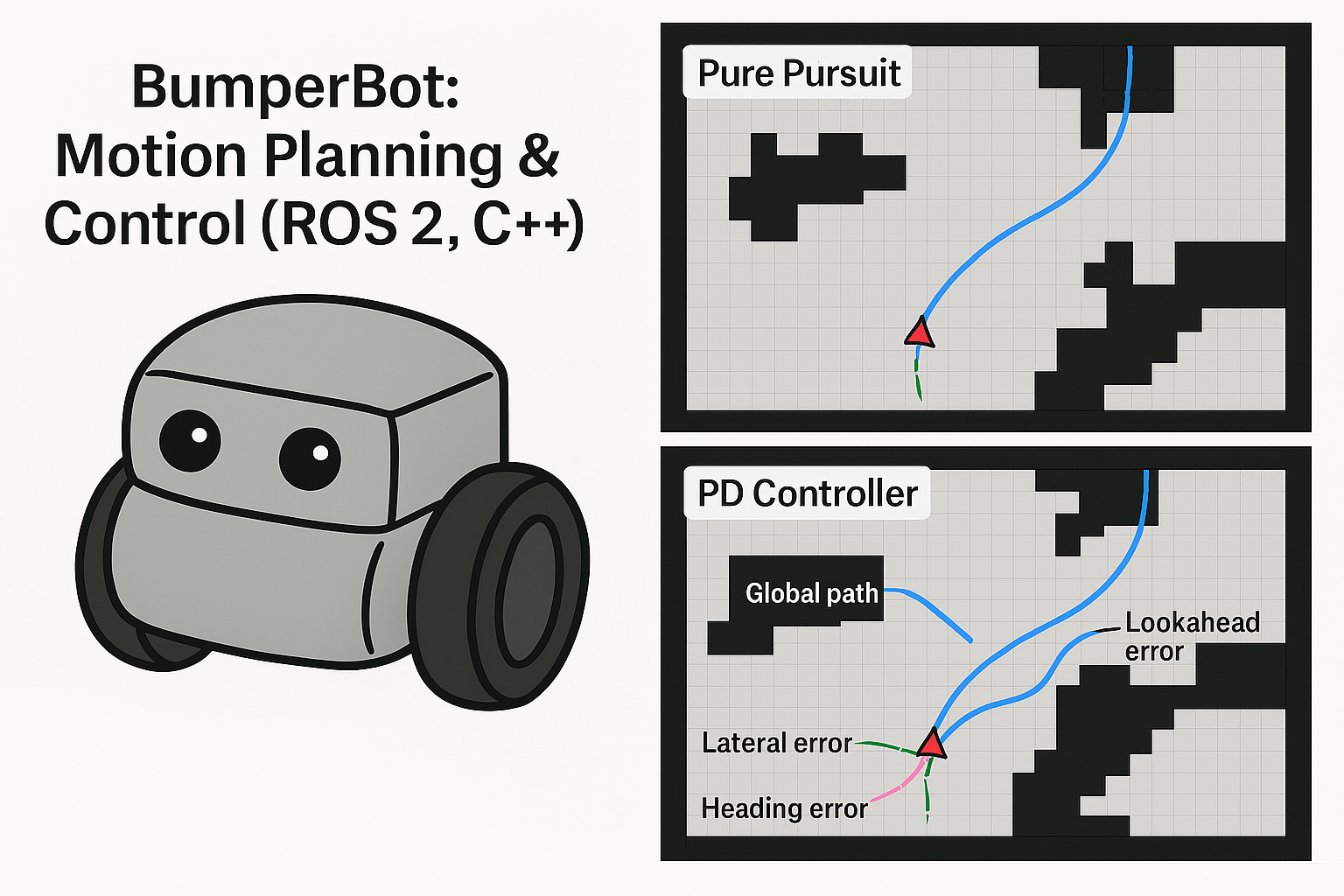 | ROS 2 Motion Planning Framework (C++ Implementation) This project implements a complete navigation pipeline, starting with global path planning and followed by local motion control. The global planner uses the A* algorithm, developed from scratch in C++, to compute an optimal path on an occupancy grid map. The planner runs as a ROS 2 node, subscribing to /map and /goal_pose topics to generate collision-free paths in real time. After generating the global path, two different motion planning strategies were implemented for trajectory tracking:
|
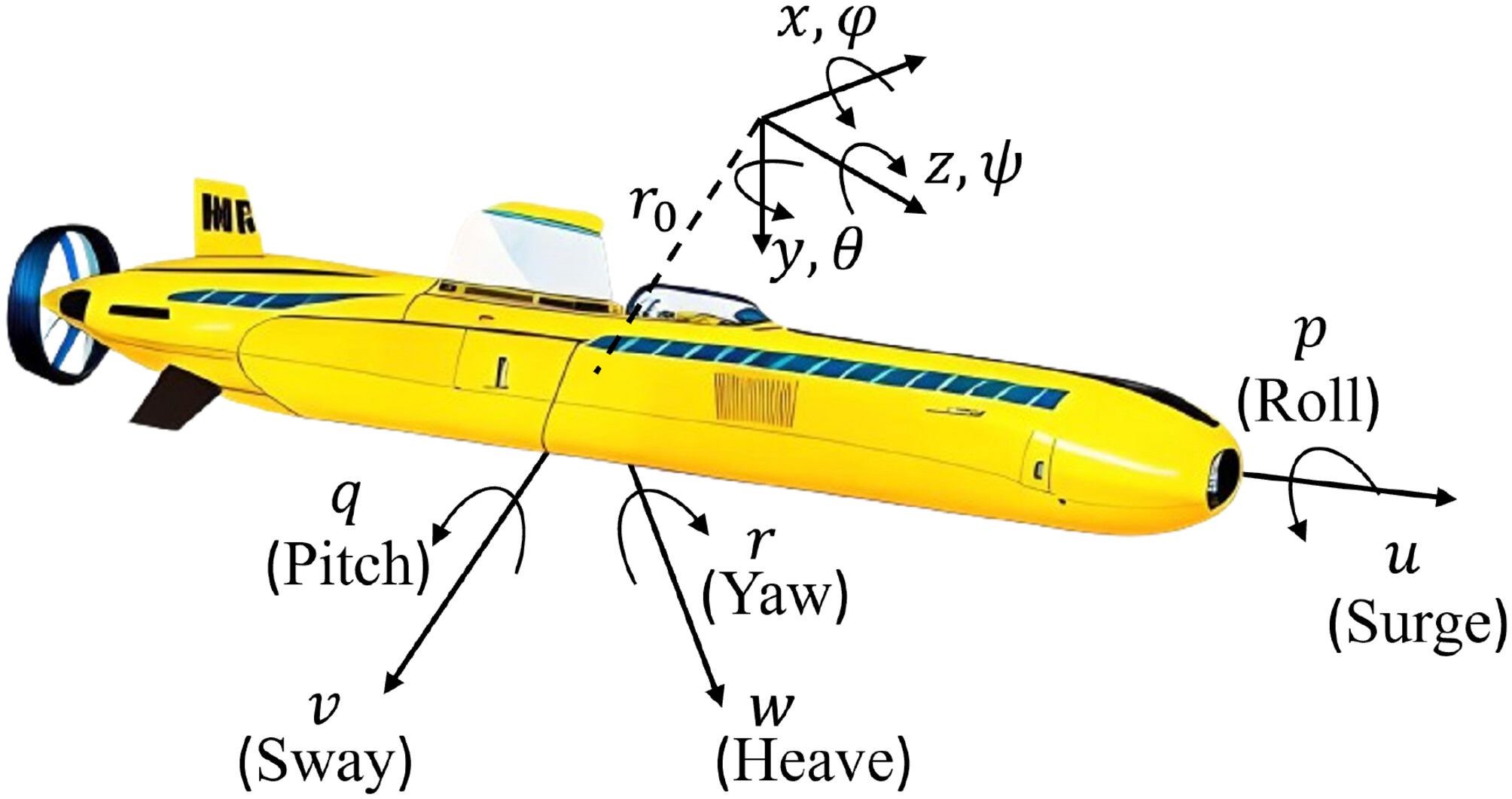 | Multi-Tasking Deep RL-Based Optimal Control of 6-DoF Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Developed a reinforcement learning-based control framework for safe and optimal tracking of 6-DoF AUVs. The approach integrates an MNN-based actor-critic method with backstepping and Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) optimization to derive optimal control policies. Safety is ensured through Barrier Functions (BFs) and Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) integrated into learning update laws, while Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) prevents catastrophic forgetting in multi-task scenarios. Simulations validate the system’s stability, adaptability, and effectiveness in dynamic underwater environments. |
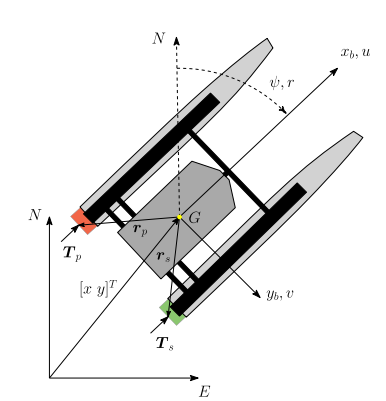 | Explainable Multi-Model Safety-Aware Deep RL Output Feedback Control with Obstacle Avoidance and A* Path Planning for Autonomous Surface Vessels Developed an Explainable safety-aware deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based control framework for optimal trajectory tracking of Autonomous Surface Vessels (ASVs). The framework employs a multilayer neural network (MNN) observer for state estimation and integrates Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) into the Hamiltonian via the Lagrangian multiplier to enforce safety constraints. An actor-critic MNN, optimized using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), stabilizes learning by mitigating the vanishing gradient problem. Additionally, a safe lifelong learning (SLL) scheme based on multiple models prevents catastrophic forgetting across varying ASV dynamics. The framework also incorporates an A* path planning module for generating collision-free trajectories and a real-time obstacle avoidance strategy for safe navigation. SHAP analysis is used to enhance interpretability by identifying critical features in the optimal policy. Simulations on an underactuated ASV model demonstrate that SLL improves performance, reducing cumulative costs by 17% and RMS tracking error by 32% compared to a non-SLL control scheme. |
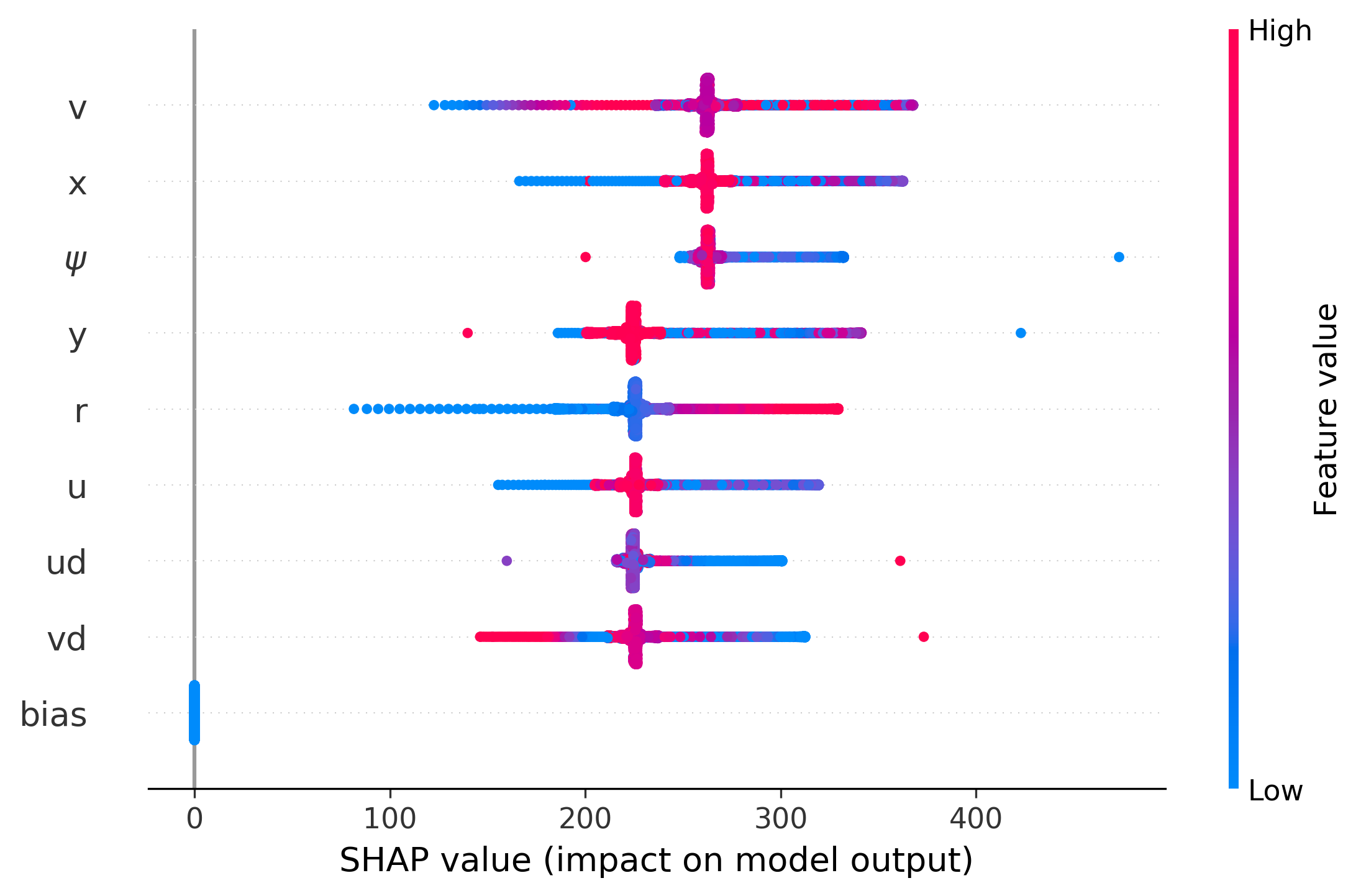
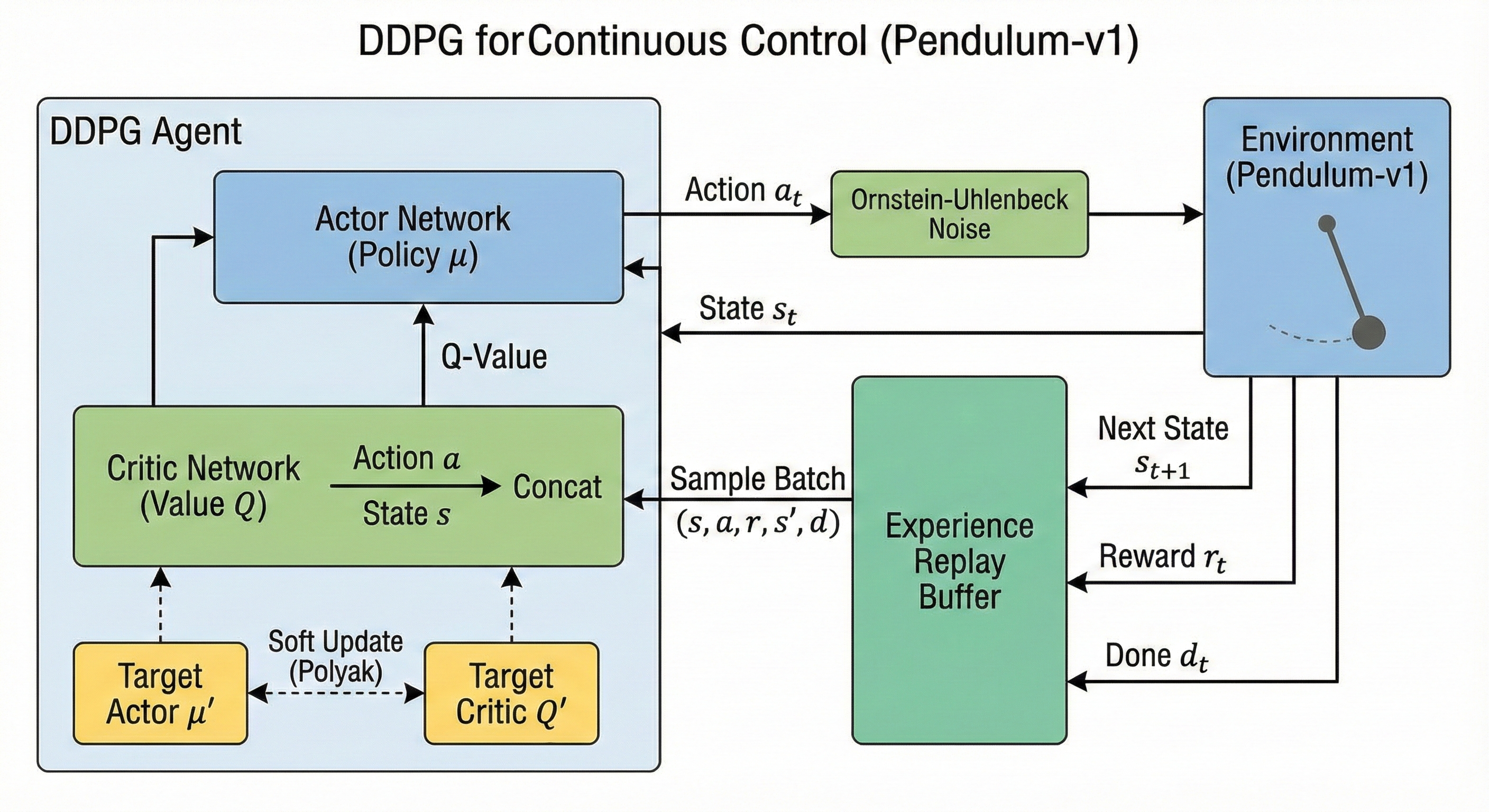 | Deep Reinforcement Learning: DDPG for Continuous Control Implemented a robust Deep Reinforcement Learning framework (DDPG) using TensorFlow and the Keras Functional API to solve continuous control benchmarks (Gymnasium Pendulum-v1). The architecture utilizes a model-free Actor-Critic approach with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU) process noise to optimize exploration in physical tasks with inertia. System stability is achieved through an optimized Experience Replay buffer for off-policy learning and Polyak averaging (soft updates) for target network synchronization, ensuring convergence in high-dimensional continuous action spaces. |
